As the Gold Coast’s premier laser cutting service provider, Emery Laser understands the importance of utilising the right materials for each project. Among the various metals we work with, aluminum stands out as a versatile and highly sought-after choice for laser cutting applications. In this blog post, we’ll explore the benefits and uses of aluminum in laser cutting.
Aluminum is a lightweight, non-toxic, and highly corrosion-resistant metal, making it an attractive choice for various industries. Its low density, combined with its strength and durability, contributes to its widespread use in applications where weight reduction is crucial, such as aerospace and automotive sectors. Additionally, aluminum’s high thermal conductivity and reflective properties present unique challenges and opportunities in laser cutting processes.
One of the primary challenges in laser cutting aluminum lies in its high reflectivity and thermal conductivity. The reflective nature of aluminum can cause the laser beam to scatter, potentially damaging the laser system or compromising the cut quality. Furthermore, aluminum’s high thermal conductivity allows for rapid heat dissipation, making it difficult to achieve the necessary temperature for melting and vaporisation.
To overcome these challenges, researchers and industry experts have developed specialised techniques and equipment. High-power fiber lasers and pulsed lasers have proven effective in cutting through thicker aluminum sheets, as their high energy density can overcome the material’s reflectivity and thermal conductivity.
Despite the challenges, laser cutting aluminum offers numerous advantages over traditional cutting methods, making it an attractive choice for various applications:
The unique properties of aluminum, combined with the advantages of laser cutting technology, have led to a wide range of applications across various industries:
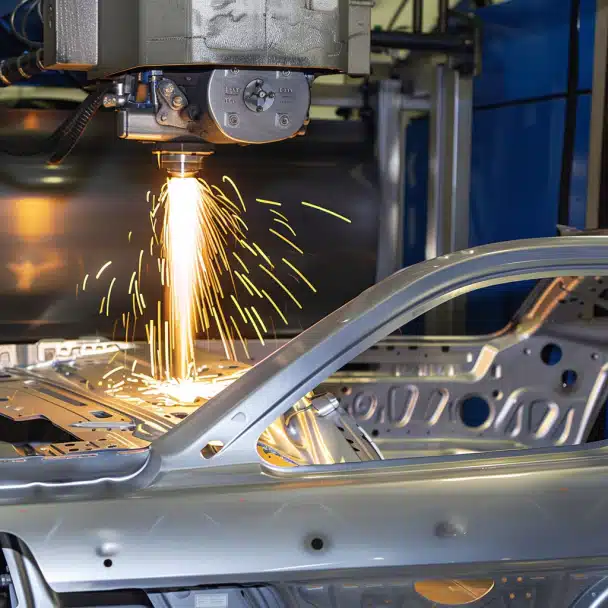
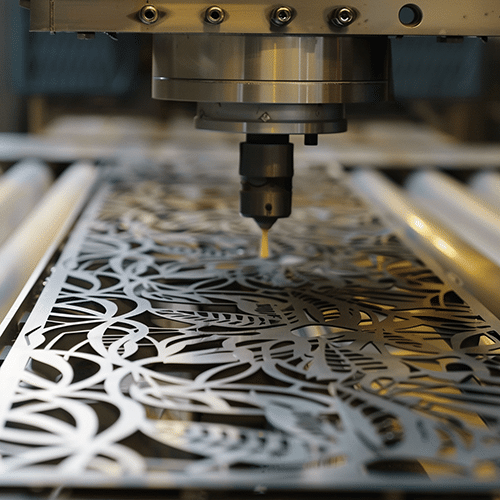



Ready to experience the versatility and precision of laser-cut aluminum for your next project? Contact Emery Laser today to discuss your requirements and request a quote.
References:
Polmear, I. J. (2005). Light alloys: From traditional alloys to nanocrystals. Elsevier.
Hirsch, J., & Al-Samman, T. (2013). Superior light metals by texture engineering: Optimizing aluminum and magnesium alloys for specific applications. Acta Materialia, 61(3), 818-843.
Wandera, C., Kujanpää, V., & Salminen, A. (2011). Laser cutting of aluminium alloy 6082. Journal of Laser Applications, 23(1), 012002.
Yilbas, B. S. (2008). Laser cutting of thick aluminum alloy: Modeling and experimental investigation. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 199(1-3), 322-330.
What You Need to Know About Laser Cutting Aluminum
https://theconversation.com/citing-blogs-in-academic-publications-lessons-from-urban-planning-in-covid-186251
https://www.research-integrity.admin.cam.ac.uk/research-integrity-guidance/citing-blogs-reference-sources